GNSS, GPS, DCF and ALS Antennas
Precise and reliable time synchronisation for your systems
Gorgy Time’s DCF, ALS, GPS and GNSS antennas are designed to guarantee reliable, stable and accurate time synchronisation for your critical infrastructures. Compatible with our master clocks, time servers and time distribution solutions, they ensure optimal satellite signal reception, even in demanding environments.
Thanks to our recognised expertise in time measurement and industrial synchronisation, we offer robust, secure antennas tailored to the needs of the most sensitive sectors: transport, energy, industry, defence, healthcare, finance, and public institutions.
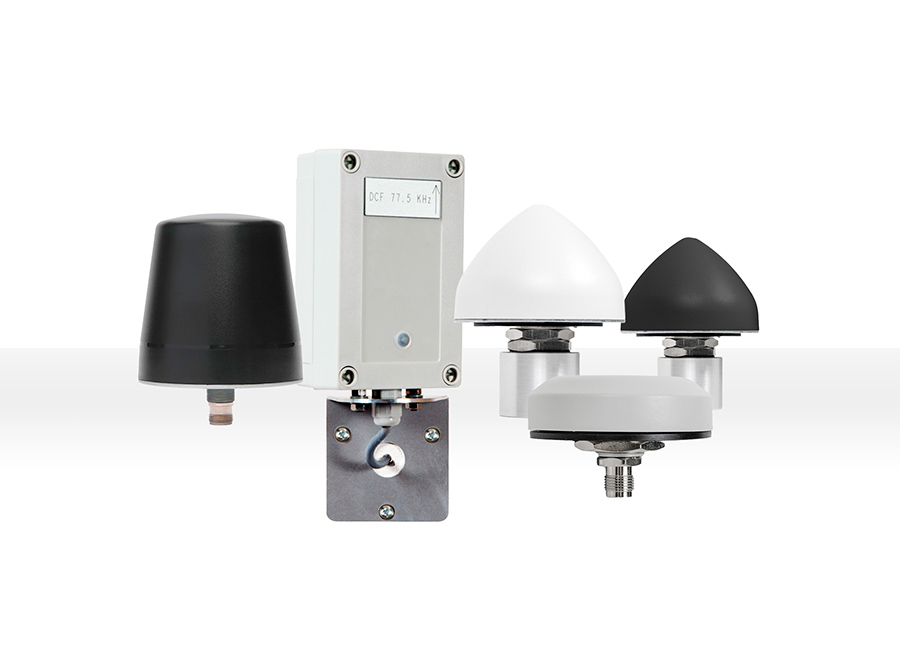

Which antenna should you choose for your synchronisation system?
Multi-constellation GNSS antennas (GPS, Galileo, GLONASS)
Multi-constellation GNSS antennas are designed to simultaneously receive signals from several satellite systems such as GPS, Galileo, GLONASS and BeiDou. This multi-constellation capability makes it possible to use a greater number of satellites at any given time, significantly improving signal availability and reliability.
By combining GPS, Galileo, GLONASS and BeiDou constellations, these antennas provide optimised global coverage, including in constrained environments such as dense urban areas, industrial sites and critical infrastructures. Simultaneous reception of multiple signals reduces the risk of loss of synchronisation due to satellite masking, interference or local disturbances.
Multi-constellation GNSS antennas therefore represent an ideal solution for demanding time synchronisation applications, ensuring higher accuracy, improved service continuity and enhanced robustness against signal uncertainties.
Local radio receivers (DCF, ALS)
Local radio receivers, such as DCF and ALS solutions, differ from satellite-based synchronisation technologies (GPS and GNSS) through their terrestrial transmission mode. DCF and ALS antennas receive a long-wave radio signal transmitted from fixed ground-based stations, unlike GNSS antennas, which receive satellite signals.
- DCF technology has historically been used in Germany, with a transmitter located near Frankfurt. These systems are geographically dependent: their range and reliability depend on the distance from the transmitter, the electromagnetic environment and local conditions.
- ALS technology, formerly France Inter, is used on the French market, with a transmitter located in Allouis, in central France.
ALS receivers and DCF antennas therefore provide an alternative or complementary solution to GNSS systems, particularly relevant for installations located in specific areas, when satellite signal access is limited, or when an independent time source separate from space constellations is required.
These ALS or DCF antennas ensure independent control of critical infrastructures while maintaining optimal performance and contributing to strengthened national sovereignty.

GPS Converter Antenna
The GPS converter antenna combines a flat antenna and a frequency converter, which converts the high-frequency, phase-modulated spread-spectrum GPS signal into an intermediate frequency.

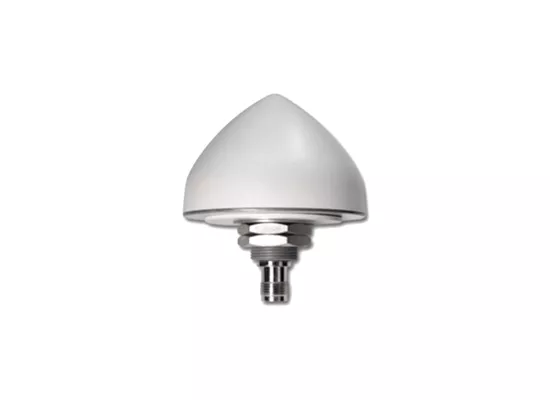
GPS Antenna
This GPS antenna combines a flat antenna and a frequency converter, which converts the high-frequency, phase-modulated spread-spectrum GPS signal into an intermediate frequency. Professional-grade GPS L1 antenna housed in a compact, conical enclosure.

GPS Hardmount Antenna
The Hardmount antenna offers a permanently fixed antenna. Housed in a compact, flat enclosure, the Hardmount antenna is suitable for moving modules or applications requiring relocation. It is a miniature antenna (patch antenna) with a 25 dB pre-amplifier.

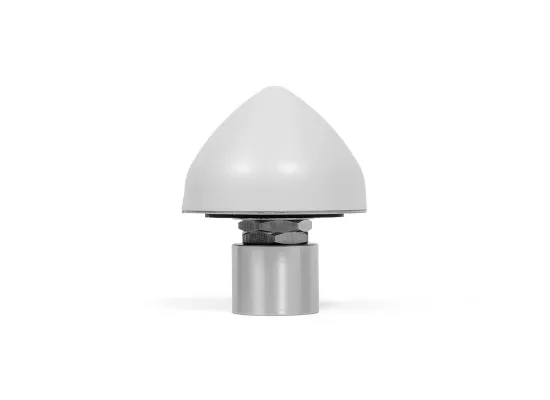
Multi-constellation GNSS Antenna
This high-precision GNSS antenna provides a synchronisation source for our time servers by retrieving time from various satellites: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and Galileo. Our GNSS antennas enable simultaneous reception of multiple satellite constellations, enhancing signal accuracy and availability, even in urban environments or adverse weather conditions.

Anti-jamming GNSS Antenna
Anti-jamming GNSS antennas are specifically designed to ensure reliable satellite signal reception in environments where the risk of intentional or accidental interference is high. Thanks to advanced architecture and highly selective filters, they reduce the impact of radio interference, jamming and signal spoofing attempts.
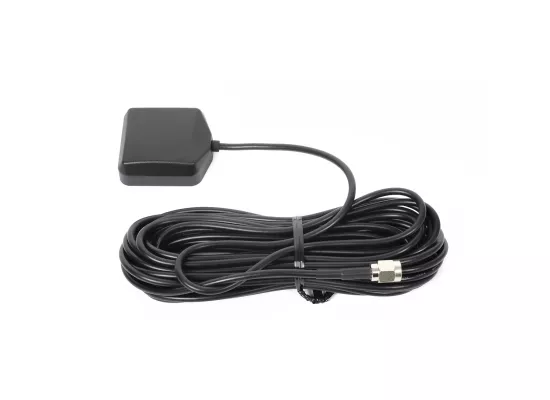

GPS Patch Antenna
The miniature GPS antenna is a flat, waterproof antenna. It features magnetic mounting for quick and reliable installation on or in vehicles, making it the ideal antenna for managing mobility and the use of embedded products.
Simplified installation and integration
Our antennas are designed for rapid commissioning:
- Wall or mast mounting
- Cables adapted to the required deployment length
- Complete kits available on request
- Gorgy Time technical assistance and support Assistance
Thanks to their optimised design, they can be installed on rooftops, masts or façades to ensure the best possible satellite visibility.
Safety accessories
Why use a lightning arrester for a GPS antenna?
A lightning arrester for GPS and GNSS antennas is an essential component to ensure the protection and reliability of your synchronisation system. Installed between the antenna and the signal reception equipment, it prevents overvoltages and electrical discharges caused by lightning or electrostatic phenomena.
By securing the coaxial line, it protects GPS or GNSS receivers and time servers against damage that could lead to service interruption, failure or time drift.
Designed to provide low signal attenuation and fast response, the lightning arrester helps ensure continuity of synchronisation in exposed industrial or outdoor environments. Its integration is therefore essential to guarantee the longevity, safety and stability of your time infrastructure.
Other antenna accessories
To complete your antenna installation, several options and accessories are available to optimise system performance and adaptability. Coaxial cables of various lengths provide flexible installation while ensuring low signal loss.
The signal splitter allows multiple devices to be supplied from a single antenna, while the line amplifier compensates for attenuation over long distances.
Finally, mounting kits facilitate robust and durable installation, ensuring optimal satellite exposure. These solutions make it possible to precisely adapt the system architecture to your technical environment and operational requirements.
- AccuracyImage
Most of Internet-based time servers have not the level of accuracy required to be used for synchronisation: our systems feature an accuracy from a hundred of milliseconds down to tens of nanoseconds.
- SecurityImage
Our products use fine corrections in order not to trigger security alerts in the case of loss of reference of the time information. The administrator is notified if a significant offset is detected.
- Continuity of serviceImage
Our time centres and time servers operate redundantly, 24h a day with the hot plug principle. The different racks can be changed while operating without requiring the whole installation to stop.
Frequently Asked Questions about Synchronisation Antennas
What is the difference between a GPS antenna and a GNSS antenna?
A GPS antenna receives signals from the GPS constellation (United States), whereas a GNSS antenna is capable of receiving signals from multiple satellite constellations (GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, BeiDou). GNSS antennas provide better signal availability, higher accuracy and greater robustness against interference and disturbances.
How can reliable time synchronisation be ensured?
Reliable time synchronisation relies on several key factors: a high-quality antenna that is correctly positioned, good sky visibility, appropriate cabling, and reception equipment that is compatible with the required signals.
Can a synchronisation antenna be installed inside a building?
A GPS or GNSS antenna must be installed outdoors with a clear view of the sky. Indoor installation is possible with an ALS antenna in France, provided it is located close to a window.
What is the difference between a mono-constellation GPS antenna and a multi-constellation GNSS antenna?
A mono-constellation antenna receives only GPS signals, whereas a multi-constellation GNSS antenna simultaneously receives several satellite systems. This diversity improves accuracy, reduces the risk of signal loss and ensures more stable synchronisation, particularly in complex and critical environments.
How can reliable time synchronisation be ensured in the event of a signal outage?
To ensure continuity of synchronisation in the event of a GPS or GNSS signal loss, it is recommended to use equipment featuring a high-stability oscillator (OCXO or rubidium), time holdover mechanisms, and a redundant time source.



